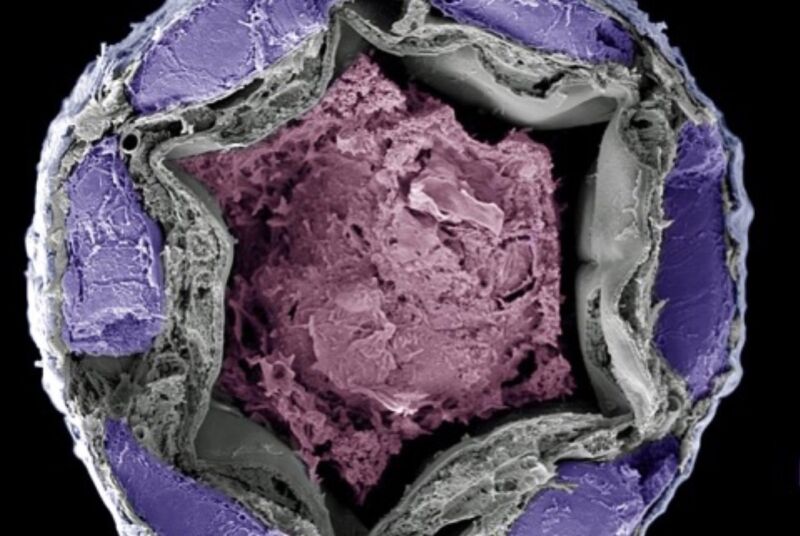
Enlarge / Who doesn't thrill to the sight of a microscopic cross-section of a beetle's rectum? You're welcome. (credit: Kenneth Veland Halberg)
There's rarely time to write about every cool science-y story that comes our way. So this year, we're once again running a special Twelve Days of Christmas series of posts, highlighting one science story that fell through the cracks in 2023, each day from December 25 through January 5. Today: red flour beetles can use their butts to suck water from the air, helping them survive in extremely dry environments. Scientists are honing in on the molecular mechanisms behind this unique ability.
The humble red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum) is a common pantry pest feeding on stored grains, flour, cereals, pasta, biscuits, beans, and nuts. It's a remarkably hardy creature, capable of surviving in harsh arid environments due to its unique ability to extract fluid not just from grains and other food sources, but also from the air. It does this by opening its rectum when the humidity of the atmosphere is relatively high, absorbing moisture through that opening, and converting it into fluid that is then used to hydrate the rest of the body.
Scientists have known about this ability for more than a century, but biologists are finally starting to get to the bottom (ahem) of the underlying molecular mechanisms, according to a March paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Science. This will inform future research on how to interrupt this hydration process to better keep red flour beetle populations in check, since they are highly resistant to pesticides. They can also withstand even higher levels of radiation than the cockroach.
No comments:
Post a Comment